The Ultimate Guide to eCommerce Business Models (B2B, B2C, DTC & More)
Explore the different eCommerce business models—B2B, B2C, DTC, B2G, and more. Learn how to choose the right model for your online business and scale with modern strategies.

Various business models exist in e-commerce, each with unique advantages, challenges, and requirements. It can be difficult to identify which one is the best fit for your use case.
The following article combines research, dry definitions, suggestions gathered from our clients, and our in-house and world-famous brand examples to help you make that decision a little easier.
What Is an eCommerce Business Model?
An eCommerce business model is the strategic framework that defines how an online business operates, delivers value, and generates revenue. It determines:
- Who you sell to (B2C, B2B, B2G, etc.)
- How you sell (direct sales, marketplaces, subscriptions)
- How you make money (one-time purchases, recurring revenue, commissions)
Essentially, your business model shapes the foundation of your eCommerce venture, from product sourcing and pricing to marketing strategies and customer relationships.
The 5 Major eCommerce Business Models
Selecting the right eCommerce business model is not just about selling products—it’s about designing a sustainable, scalable, and profitable business. The better you align your model with market demand, revenue strategies, and technology, the higher your chances of success.
There are five major eCommerce business models, with all the shades in between.
Business Model | Target Audience | Example Companies | Key Advantage |
B2C | Consumers | Amazon, Nike | Direct brand control |
B2B | Businesses | Alibaba, Salesforce | High-volume orders |
B2B2C | Both | Shopify, Instacart | Scalable partnerships |
B2G | Government | SAP Ariba | Large contracts |
C2C | Consumers | eBay, Etsy | Peer-to-peer flexibility |
Let’s cover them a bit in depth.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
A business-to-consumer business markets products and services directly to consumers.
Every time you purchase anything from a store, eat lunch at a restaurant, attend a movie at the theater, or get a haircut, you engage in a B2C transaction. These businesses offer goods and services to you, the customer directly. This is also known as the direct-to-consumer (D2C) approach.
Businesses that want to use the B2C eCommerce model must have a flexible eCommerce platform to quickly adjust to changing customer demands. Service delays and other issues can be avoided in this way.
Revenue vise, companies in B2C are into Direct Selling, which is the most common model in which people buy goods from online retailers. Think of Target or Gap, Nike and Macy's, and even Porche. You pay for the product directly.
Or operate as online intermediaries, i.e., connecting sellers and customers and taking a percentage of every purchase for themselves. Websites like Etsy, eBay, and Booking.com fall into this category.
Or offer a Subscription to their service, i.e., require a paid subscription in exchange for unrestricted access to their content. These are usually entertainment services such as Netflix and HBO Max.
💎How Crystallize helps.
B2C businesses need speed, scalability, and personalization—this is where Crystallize’s headless commerce engine excels. It enables B2C brands to create seamless and flexible shopping experiences.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC)
The Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) business model has emerged as a game-changer in the retail industry. By bypassing traditional intermediaries and selling products directly to consumers, businesses can gain greater control over their brand, customer experience, and revenue streams.
Even well-known brands are opting out of DTC marketing strategies.
Business-to-Business (B2B)
The business-to-business model means a company sells its products or services to other companies. A B2B transaction typically has a longer sales cycle but higher order values and more recurring purchases.
B2B eCommerce can be divided into two categories: vertical and horizontal.
Vertical B2B companies sell goods and services specifically within one industry. The perfect example is the car manufacturing industry: one company makes steel and only sells it to car manufacturers, another provides tires, and another provides engines.
Horizontal B2B businesses serve a wide range of buyers across various industries and do not specialize in any particular product or service.
Alibaba, for example, is the world’s largest B2B marketplace, connecting manufacturers with retailers globally. Any software vendor like headless commerce platform Crystallize is a B2B e-commerce model.
Direct purchase and subscription models are the most popular revenue approaches in B2B.
💎How Crystallize helps.
With our powerful APIs, B2B companies can easily streamline bulk orders and personalized pricing.
Business-to-Business-to-Consumer (B2B2C)
B2B2C is a business model in which a company sells its product or service to an end customer in partnership with another organization. An example of a B2B2C arrangement is when a wholesale distributor sells merchandise to retail stores, which then sell the merchandise to end users.
The main advantages of this business model are that it provides new economic opportunities that would otherwise be impossible to access, improves convenience, combines industries, and increases customer access.
It enables brands to reach a wider audience and scale quickly while still maintaining some brand presence. Instacart is a grocery B2B2C marketplace connecting stores with consumers. A food delivery model, where restaurants sell via Glovo, DoorDash, UberEats, etc., to end customers, is another example of B2B2C in practice.
💎How Crystallize helps.
Relying on headless architecture enables businesses to sell via third-party retailers seamlessly while keeping their product data in a single place. You can also connect wholesalers, logistics providers, and DTC channels while ensuring brand consistency.
Business-to-Government (B2G)
When a company sells its products and services directly to a government agency, it falls under the business-to-government model. Due to government agencies' supervision and intervention, the B2G eCommerce model is more complex and demands strict compliance with business laws and conditions.
With eCommerce, B2G businesses are mainly in the fields of electronics, telecommunications, and infrastructure. AWS GovCloud is a perfect example.
💎How Crystallize helps.
Crystallize does not focus on B2G, but our APIs can enable government-compliant procurement platforms.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
In C2C eCommerce, consumers sell goods or services directly to other consumers. Third-party websites or marketplaces most often facilitate transactions on behalf of buyers and sellers.
Best-known examples of C2C include eBay and Amazon, which act as both B2C and C2C marketplaces. Since its launch in 1995, eBay has been one of the leading marketplaces for consumers to sell and buy from each other.
This model has benefits, including increased profitability, a larger customer base, and convenience for both parties. However, its disadvantages include platform fees, potential fraud, and low-quality control.
💎How Crystallize helps.
Flexible APIs for peer-to-peer transactions and customizable payment and commission structures scream that C2C is possible. However, we don't have the C2C project in our hands yet.
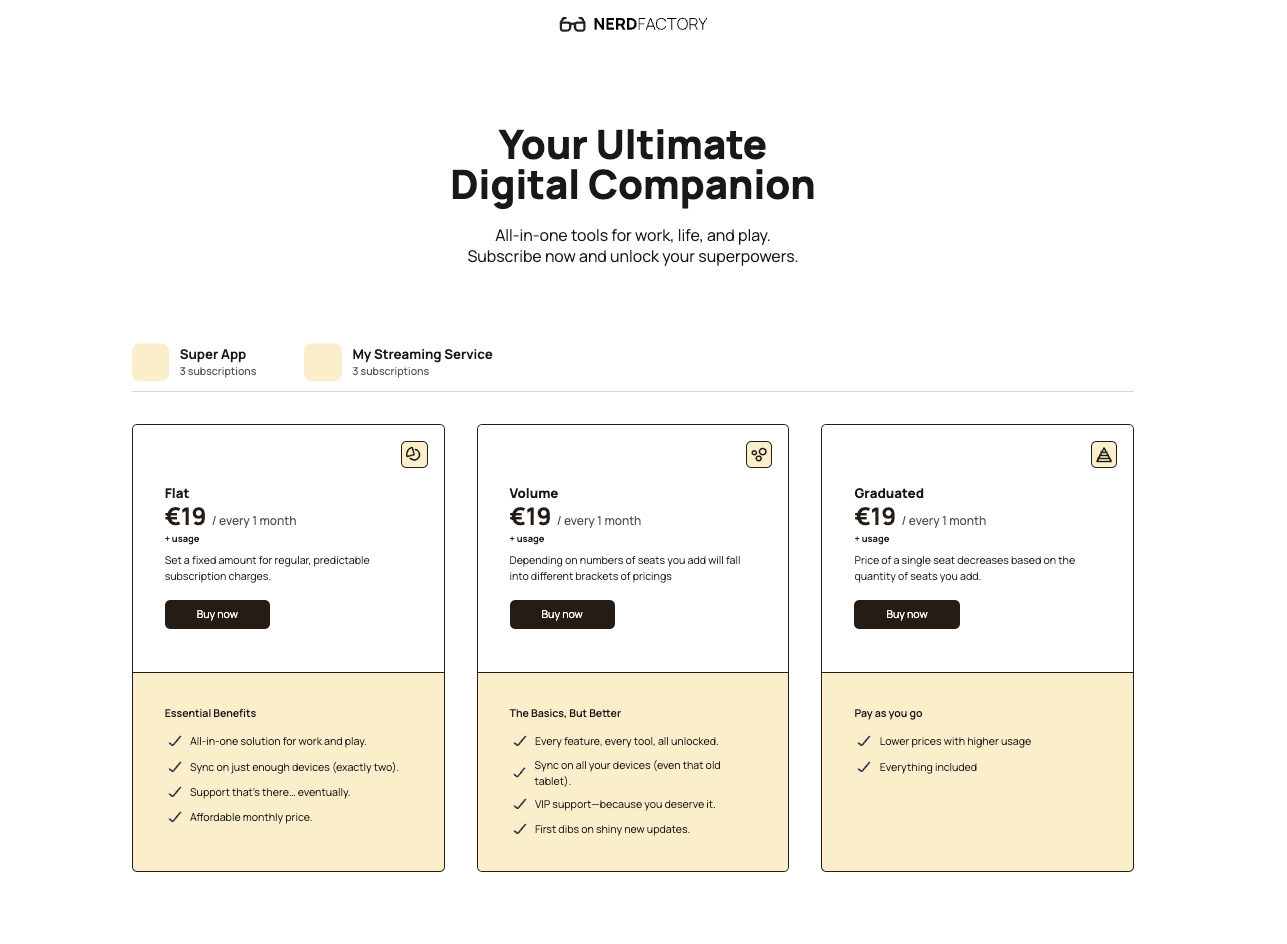
Revenue Models
Now that you know who you’re selling to and how (i.e., which business model best suits your needs), it’s time to identify your revenue model or how you’ll make your profits.
Choosing the right revenue model is just as important as selecting your eCommerce business model. It determines how your business generates income, whether through direct sales, subscriptions, commissions, or other monetization strategies.
Revenue Model | Definition | Example Companies | Best for |
Direct Sales | Sell products directly | Nike, Apple | B2C, B2B |
Dropshipping | Supplier ships directly to customers | AliExpress, Oberlo | B2C, C2C |
Subscription | Recurring revenue model | Netflix, Crystallize, Dollar Shave Club | B2C, B2B, DTC |
White Label | Rebranding third-party products | Beauty brands, Shopify | B2B, B2C |
Private Label | Manufacturing under own brand | Amazon Basics | B2C |
Wholesale | Bulk sales to businesses | Alibaba, Costco | B2B |
💎How Crystallize helps.
Crystallize supports all major revenue models, including subscriptions, bulk pricing, discounts, and headless marketplace integrations. Fully flexible pricing allows for a range of pricing models.
Direct Sales
Direct sales involve selling your product or service directly to consumers, managing payment, and completing the order fulfillment pipeline.
Dropshipping
If you’ve ever Googled anything eCommerce, you’ve probably seen a dropshipping course ad or two. It has become trendy in recent years due to its simplicity: you don’t have to manage inventory, you don’t have to have a warehouse or deal with packaging -- but you have to have an outstanding supplier.
You only have to set up a storefront, list your products, and charge your customers for them. Once an order is placed, your supplier takes care of the rest.
Remember that if they’re particularly slow, you’ll open yourself up to bad reviews (remember reviews / online reputation management are crucial for your local SEO efforts and add up to your brand image) and/or product quality complaints if it is unsatisfactory. Additionally, dropshipping will typically have pretty thin profit margins.
Subscription
Subscription businesses have the most stable revenue streams. They provide ongoing services in exchange for recurring customer payments.
Depending on the type of product or service you sell, you can opt for a replenishment subscription service (usually for commodity products like groceries or cosmetics), a curation subscription service (for collections of products personalized to customers), or an access subscription service (for exclusive access for paying customers).
Subscription offers excellent potential, but success with it does not come overnight. The topic itself is gargantuan, and I invite you to check our Ultimate Guide to Subscription eCommerce for an in-depth view of everything subscription.
📄 Building a subscription eCommerce business.
Experiment with the perfect infrastructure for flexible pricing, recurring billing, and personalized content experiences with Crystallize. Kickstart your subscription commerce journey with Crystallize Next.js e-commerce starter written in TypeScript.
This accelerator is powered by Discovery API, which helps you launch and scale your subscription business quickly.
📄 Crystallize Next js subscription commerce starter.
White Labels
In white labeling, you’d find a product that another company makes and offers white labels. You then pay that company for the white label, design and label your product, and sell it as your own.
You’ll frequently encounter this model in the beauty industry or online blogging platforms like Tumblr or WordPress, allowing you to set your custom URL if you pay for the white label.
Private Labels
This model is fairly straightforward. If you don’t have your production line, you can contact a manufacturer and pay them to create the product for you. They can then either ship the product directly to the customer, to a third-party retailer like Amazon, or you so that you can sell it.
This can work well as long as you identify a reliable manufacturer.
Wholesale
Typically, a wholesaler sells products in bulk at a discounted price to other businesses. However, those who opt to sell bulk products at a discount to businesses and separate pieces at the right price to consumers can significantly increase their profit margin (and their workload).
Selecting the Right eCommerce Business Model
Your product/service is the setting stone. However, selecting the right eCommerce business model is a strategic decision that shapes your brand’s success, scalability, and profitability. It reflects your market understanding, customer-centricity, and long-term vision.
There is no way around it, TBH. So the better you can nail product-market fit, in theory at least, the more likely you’ll adopt a model that fits your use case.
Still, a couple of best practices and contemplative questions can help you understand solutions and make better decisions.
Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand demand, competition, and customer preferences. This will help you recognize your target audience's pain points and help validate your target audience before investing heavily in your business model.
- Question: What unmet needs of the market can your business address? How well do you understand your target customer’s preferences and behaviors?
Develop a compelling value proposition that underscores what sets you apart from the competition beforehand.
- Question: What unique value does your solution offer to its users? How does your value proposition compare to your competitors?
Embrace technology that augments the user experience, streamlines operations, and provides data-driven insights. This includes considering the adoption of headless commerce for greater flexibility and personalized user experiences.
- Question: What technological infrastructures and platforms align with your product and preferred e-commerce business model? How adaptable is your technology stack to the evolving market demands?
Establish a clear monetization strategy. Once you've determined who you’re selling to and what you’re offering, you need to define how your business will generate revenue. Whether it’s a subscription model, a one-time purchase, or a freemium model, ensure that your pricing is competitive yet profitable.
- Question: What pricing strategy will optimize your revenue while remaining attractive to your customers? How does your monetization strategy align with your market position?
Build strategies for customer engagement and retention. A satisfied and returning customer is a valuable asset. Engage customers through personalized experiences, quality service, and value-added features.
- Question: How will you measure and enhance customer satisfaction? What strategies do you have in place to encourage repeat business?
Ensure your business operations are agile and scalable to adapt to market changes. Building a business model that can scale with growth is imperative for long-term success.
- Question: How is your e-commerce business model poised to handle growth and market fluctuations? What processes have you established to remain agile in responding to market dynamics?
Pondering over these questions while adhering to the outlined best practices will help you choose the best business model and engender a comprehensive business plan.
The Wrap
Product/service comes first. Your business is most likely one of the possible combinations of these, and its combination may impose certain technological and promotional restrictions (or rather, audience expectations).
This does not mean that you should conform to these restrictions. Not at all! The best brands in the world defy convention and are successful because of it.
Explore how Crystallize powers modern eCommerce models—SCHEDULE a demo today, and we’ll show you what makes Crystallize a powerful product story engine well suited for your business.
Or, why not SIGN UP for FREE and start building the website yourself?
Follow the Rabbit🐰

Comprehensive Guide to Modern eCommerce Web Development: Trends, Approaches, and Best Practices
Explore the latest trends, development approaches, and best practices to build high-performing online stores in modern e-commerce web development.

10 Best E‑commerce Platforms for Developers and Business Owners in 2025
Explore 10 leading e‑commerce platforms for 2025—including monolithic SaaS solutions like Shopify, BigCommerce, and Magento; composable headless options such as CommerceTools and Commerce Layer; and unified GraphQL/PIM‑powered platforms like Crystallize. Match your business model, technical requirements, and budget to find the optimal balance of ease‑of‑use, performance, and flexibility.

Optimizing eCommerce Success: Best Practices for Web Development with Modern Frameworks
Unlock the potential of your online store with modern frameworks and eCommerce web development best practices for building a fast, user-friendly, and high-converting site.
