How Credit Card Authorization Works?
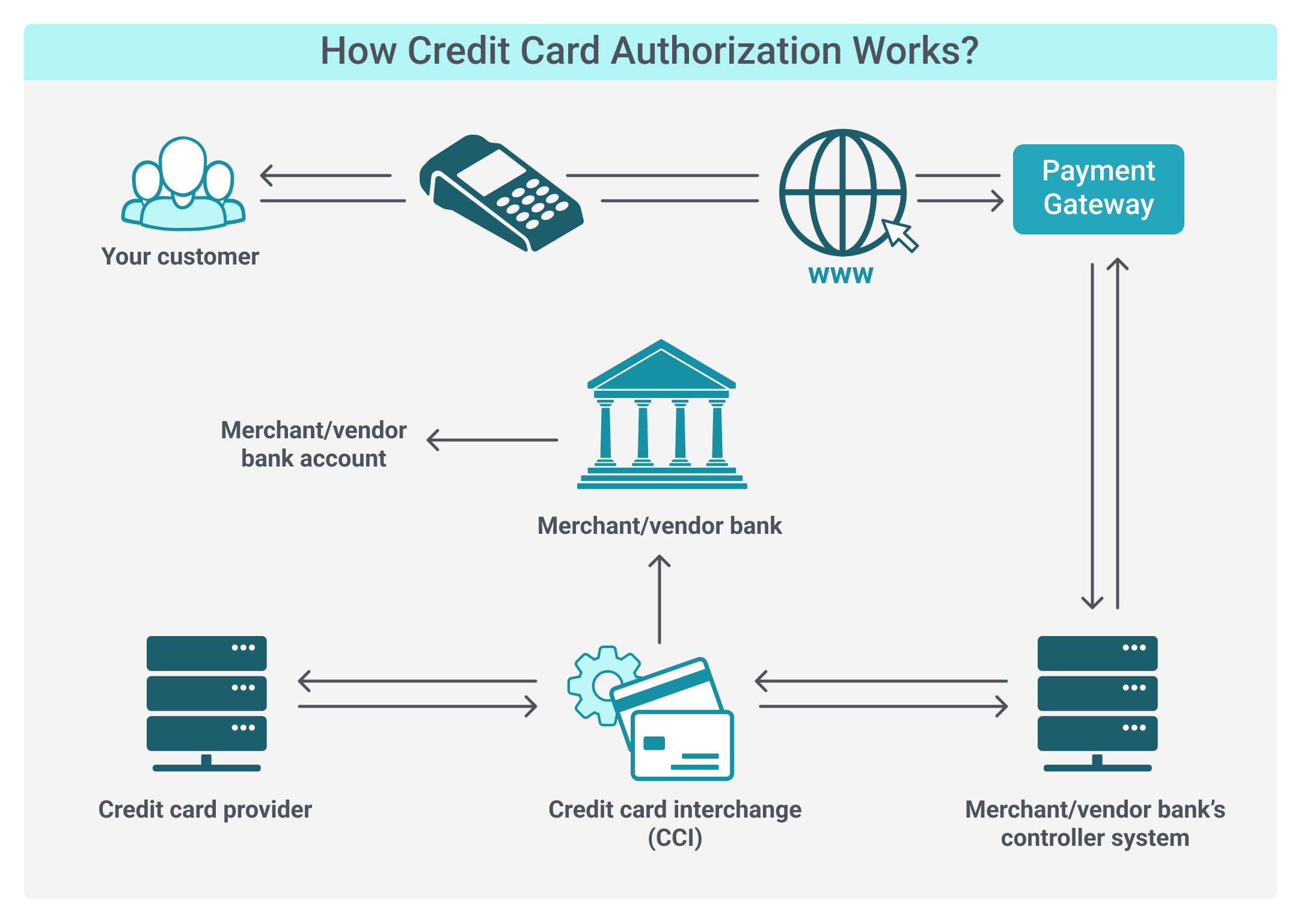
Credit card authorization is a crucial process in online transactions, enabling merchants to ensure that a customer's card has sufficient funds and is valid for purchases.
This process involves several key players, including the cardholder, merchant, acquiring bank, issuing bank, payment network, and payment gateway providers. In this technical overview, we will explore the intricacies of the online credit card authorization process and how each component works in unison to enable seamless transactions.
Initiation of Transaction
The process begins when a cardholder initiates an online transaction by providing credit card details on the merchant's website or app. The information typically includes the card number, expiration date, cardholder name, and Card Verification Value (CVV) code.
Data Encryption and Transmission
To ensure data security, the merchant's system encrypts the cardholder's information using Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols. The encrypted data is then transmitted to the acquiring bank, which acts as the intermediary between the merchant and the payment networks.
Transaction Routing
The acquiring bank routes the transaction through the appropriate payment network (e.g., Visa, Mastercard, American Express, or Discover), which then forwards the transaction request to the issuing bank. The issuing bank verifies the cardholder's information and account status.
Authorization Request
The issuing bank examines the transaction details and checks the cardholder's account for available credit, card status (e.g., active or expired), and any possible security concerns (e.g., potential fraud). Based on this analysis, the issuing bank generates an authorization response code.
Authorization Response Codes
The authorization response code is a numerical or alphanumerical code indicating the result of the transaction request. Some common response codes include:
- 00: Approved
- 05: Declined
- 14: Invalid card number
- 51: Insufficient funds
- 54: Expired card
Response Routing
The issuing bank sends the authorization response code back through the payment network to the acquiring bank, which then forwards the code to the merchant's system.
Merchant's Action
Upon receiving the response code, the merchant takes appropriate action. The merchant proceeds with the order fulfillment process if the transaction is approved. If declined, the merchant informs the cardholder of the decision and may request an alternative payment method.
Completion of Transaction
Finally, the authorized transaction is queued for settlement, which transfers funds between the acquiring and issuing banks. Settlement typically occurs within 1-3 business days when the transaction amount is debited from the cardholder's account and credited to the merchant's account.
By securely transmitting cardholder information and verifying the transaction's legitimacy, the process ensures a safe and efficient exchange of funds between cardholders and merchants.