DAM vs. CMS: Key Differences & Do You Need Both for Headless Commerce?
Digital Asset Management (DAM) systems and Content Management Systems (CMS) are both valuable for managing digital content, but they serve different purposes.
If you’re building a modern headless commerce stack, you might be wondering which one you truly need – or if you might need both. In this guide, we’ll break down the key differences, solve common pain points, and help you decide on the right approach for your business.
DAM vs. CMS at a Glance
To quickly compare, here’s an at-a-glance table highlighting the core differences between a DAM and a CMS:
| Feature | Digital Asset Management (DAM) | Content Management System (CMS) |
|---|---|---|
Primary Goal | Organize & share brand assets (files) | Publish content to websites (pages) |
Primary Users | Designers, Marketers, Sales teams | Web Editors, Developers, SEO specialists |
Asset Types | High-res videos, print graphics, source files (e.g., PSD, AI) | Web-optimized images (JPEG, WebP) and text content |
Organization | Metadata, tags, and AI-powered search for files | Page hierarchy, navigation menus, sitemaps |
Distribution | Omnichannel distribution (print, social, partner portals, etc.) | Single channel publishing (your website or app) |
At a glance: A Digital Asset Management or DAM is all about managing media files and creative assets across the organization, while a Content Management System or CMS focuses on managing web pages and structured content for online publication. Next, let’s dive deeper into why this distinction matters.
Why a CMS Media Library Isn’t Enough?
Many teams try to use a CMS’s built-in media library for all their asset management – and quickly run into headaches. A traditional CMS media library is typically just a basic repository for images and files attached to web content. This can lead to several problems for modern brands, such as asset duplicates and lost files, no version control, limited sharing and access, and performance and format constraints.
It wasn’t designed to be a full asset management solution, so teams relying on it may face disorganization, inconsistent branding, and productivity bottlenecks.
The solution > do you need both, or is there a better way?
Many organizations consider using both a DAM and a CMS together: one system for assets and another for web content. This dual approach does solve the immediate problems – you get powerful asset organization in a DAM, plus robust content publishing in a CMS. However, it also means two separate systems to pay for, implement, and maintain. Not every business has the budget or desire to manage two different platforms (and their integration).
Modern headless ecommerce platforms (like Crystallize) blur the lines by providing a unified solution. Rather than running a standalone DAM and a separate CMS, some headless systems include a native asset organizer that acts as a “lite DAM” built into the content platform. This gives you the benefits of both without the silos, ie, you can store and organize all your assets in one place with metadata tagging and optimization, without sacrificing the ability to easily use them in your product pages or blog posts.
Let's dig a bit more into both approaches.
How Headless Architecture Changes the DAM vs. CMS Debate?
Headless architecture breaks the tight coupling between CMS, DAM, and the frontend, turning content, assets, and product data into API-served building blocks instead of page-bound resources. This makes assets usable across any channel – web, mobile, in-store, or social – without duplicating systems or workflows.
As a result, the line between CMS and DAM blurs, with modern headless platforms covering parts of both via shared APIs. Add PIM into the mix, and you get a modular stack where content, assets, and product data work together cleanly, without hard dependencies or platform lock-in.
Use Case Scenarios: DAM vs. CMS vs. Both
Every organization’s needs are different. Here are a few real-world scenarios to illustrate when you might lean towards a DAM, a CMS, or an integrated approach:
Scenario A – You Need a DAM: You’re a global brand with dozens of retail partners and agencies. Each season, you produce hundreds of high-resolution photos and videos (e.g., your Spring Collection lookbook) that partners worldwide need in print-quality. In this case, a DAM system is essential. It provides a central hub where your partners can quickly grab the latest approved images, logos, and videos. The DAM ensures everyone accesses the same up-to-date assets, with permissions and expiration dates as needed. A standard CMS library would crumble under this scale and sharing requirement.
Scenario B – You Need a CMS: You’re a content-rich publisher or a niche brand running a blog and website. Your primary workload is creating articles, web pages, and landing pages, with relatively standard web images and text. Here, a robust CMS is your priority. It will help you manage editorial workflow, content scheduling, SEO, and multi-language publishing. You likely have only a small collection of images or graphics e-commerce which a basic media library can handle. Investing in a full DAM might be overkill if you don’t have a large volume of diverse assets to organize outside of the website context.
Scenario C – The Headless Commerce Sweet Spot: You’re an e-commerce brand that values rich storytelling. You have lots of product images and maybe even user-generated photos or videos. You want each product page to tell a story with beautiful media, and you need those high-res images automatically optimized for mobile, desktop, and social media without manual effort. This is the perfect use case for a headless commerce platform with an integrated DAM-like asset manager.
For example, Crystallize’s Asset Organizer lets you upload huge product images once and then serves them in the ideal format and size to every channel (web, app, social embed) via API. You get the benefit of DAM-level optimization and organization, and a powerful CMS for product content – all in one. This scenario saves you from juggling separate systems while delivering a top-notch customer experience across channels.
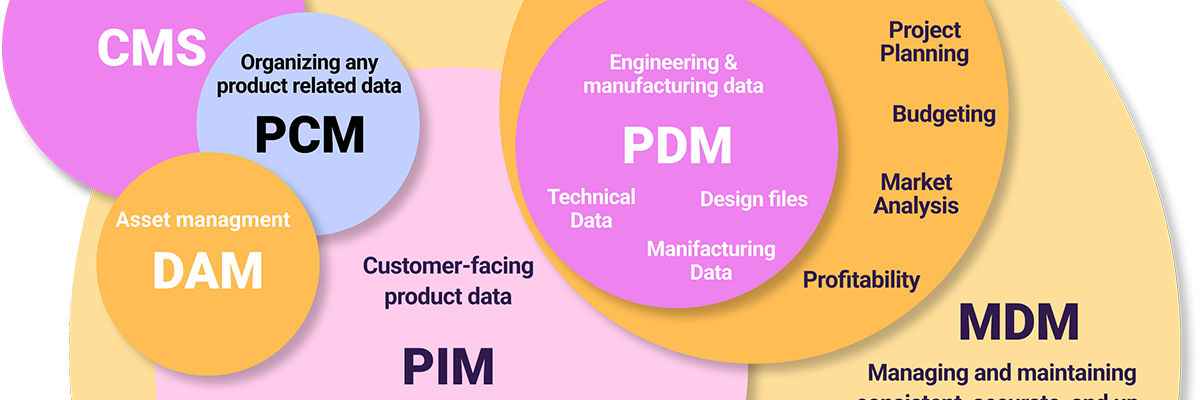
📑Managing Product Data, Customer Data and Tools You May Need Infographic.
What is PIM, and how different is it from other similar tools? We’ve tried to clear up the acronym confusion in eCommerce with the following infographic that provides you with a visual comparison of all relevant terms. Individual posts dig deeper into each term and the concept behind it.
📝READ WHAT IS PIM AND DOWNLOAD THE INFOGRAPHIC FOR FREE FROM HERE
Bringing It All Together
Choosing between a DAM and a CMS comes down to your content vs. asset needs – but thanks to headless solutions, you might not have to choose at all. If managing rich assets and content in one place sounds appealing, consider a platform that combines these capabilities.
Stop paying for separate DAM and CMS silos.
See how Crystallize handles rich assets and content in one API-first platform to support your headless commerce goals. With the right approach, you’ll save time, reduce costs, and empower your team to deliver amazing digital experiences across every channel.