Subscription commerce
Subscriptions in Crystallize let you sell products and services on a recurring basis. Instead of a single transaction, customers subscribe to receive continuous access or recurring deliveries. This supports business models ranging from subscription boxes and digital memberships to complex B2B service agreements.
The subscription engine is built to be flexible and composable. You can define contract terms, billing cycles, and renewal rules, then connect them seamlessly with your product catalog, orders, and payments. This makes it just as easy to set up a simple monthly plan as it is to model advanced usage-based or multi-tier B2B agreements.
What you gain
- Predictable revenue - Secure recurring income and improve forecasting.
- Customer retention - Build long-term relationships with customers through ongoing value.
- Operational efficiency - Automate renewals, billing, and product delivery.
- Flexibility - Support simple monthly subscriptions, usage-based billing, or custom B2B agreements.
Key concepts in Crystallize subscriptions
- Subscription plans
Predefined configurations that describe how a subscription works.
Examples: “Pro Plan, billed monthly” or a usage-based storage model.
Plans define the rules for billing frequency, usage metrics, and entitlements. - Subscription offerings
The price book that applies a subscription plan to a specific product.
This is where you connect pricing and availability to what customers actually see and purchase in your storefront. - Subscription contracts
The formal agreement between you and the customer, created when a customer subscribes.
Contracts define the start date, billing and renewal cycle, and cancellation policies. They also store payment tokens for recurring charges. - Recurring orders
Orders generated automatically according to the subscription contract’s schedule (e.g. monthly, quarterly, annually).
These orders trigger billing, invoicing, and fulfillment, ensuring the customer continues to receive the product or service.
Subscription Business Models
Subscriptions can be applied in many industries. Here are the most common categories:
- Digital subscriptions
Recurring access to digital services, charged automatically on a fixed schedule.
Examples: Netflix, Spotify, most SaaS products, including Crystallize itself. - Recurring goods
Physical products delivered to customers on a set schedule.
Examples: razors, shampoo, coffee, groceries. - Usage-based subscriptions
Charges are calculated based on how much a product or service is consumed.
Examples: Dropbox storage, mobile phone plans, electricity.
Flexible Subscription Pricing Models
Crystallize supports multiple pricing strategies so you can adapt your offering to customer expectations:
- Flat fee
A fixed recurring amount regardless of quantity or usage.
Example: $9.99/month for unlimited streaming. - Quantity-based
Customers subscribe to a defined number of units per billing cycle.
Example: 2 bags of coffee per month. - Volume discounts
Price per unit decreases as the customer subscribes to higher quantities.
Example: $10/month for up to 5GB storage, $8/month for 6–20GB. - Tiered pricing
Different tiers with bundled features or limits.
Example: Basic, Pro, and Enterprise SaaS plans.
Typical Subscription Flows
Managing subscriptions involves two main flows: initial purchase and renewals.
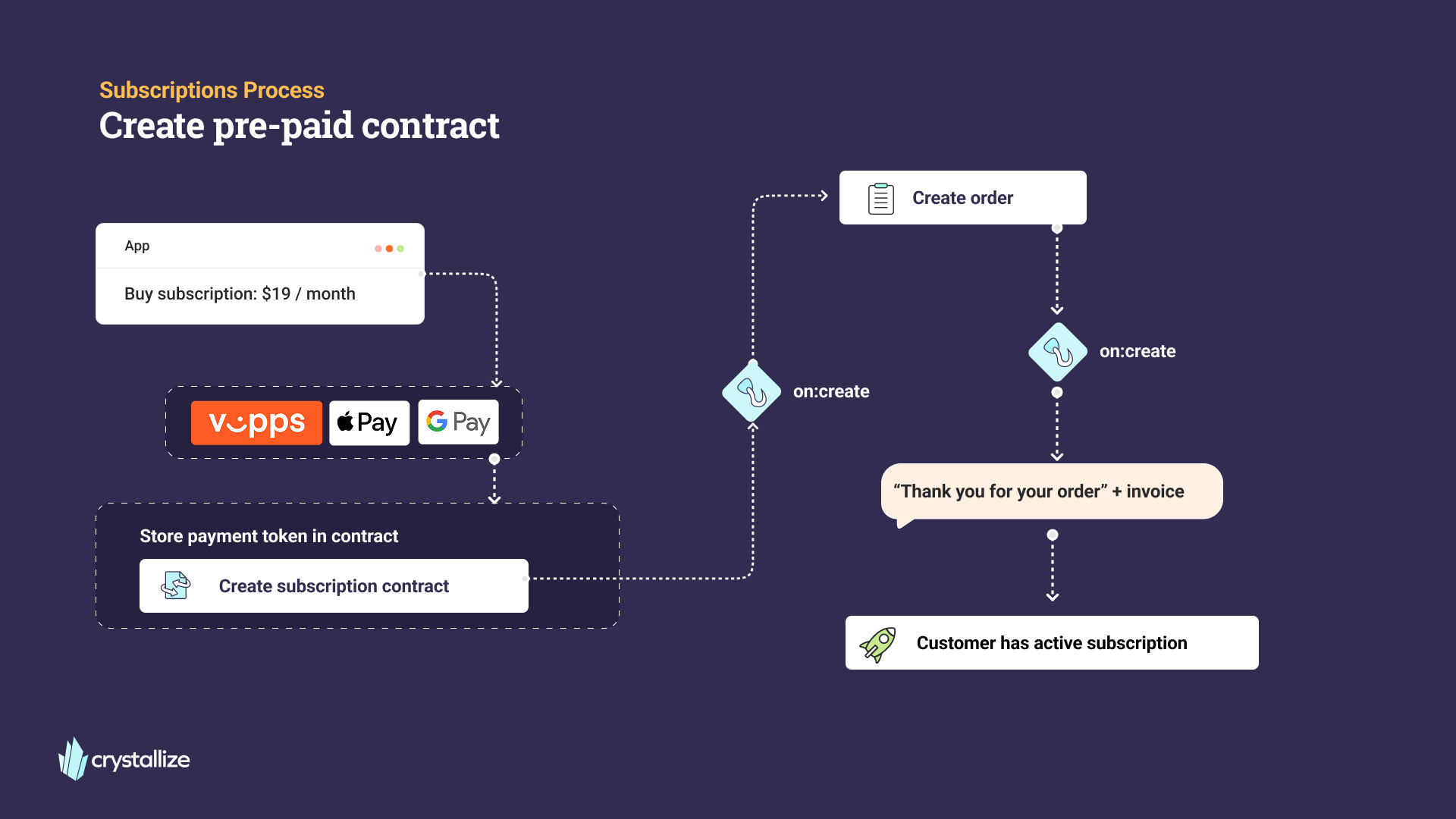
Pre-paid Subscription signup
When a customer purchases a subscription, the following happens:
- The customer selects a subscription plan in your storefront (e.g. $19/month).
- They complete the payment through a supported provider (e.g. Vipps, Apple Pay, Google Pay).
- A subscription contract is created in Crystallize, storing the payment token for future renewals.
- An order is created and an invoice is generated.
- The customer now has an active subscription.
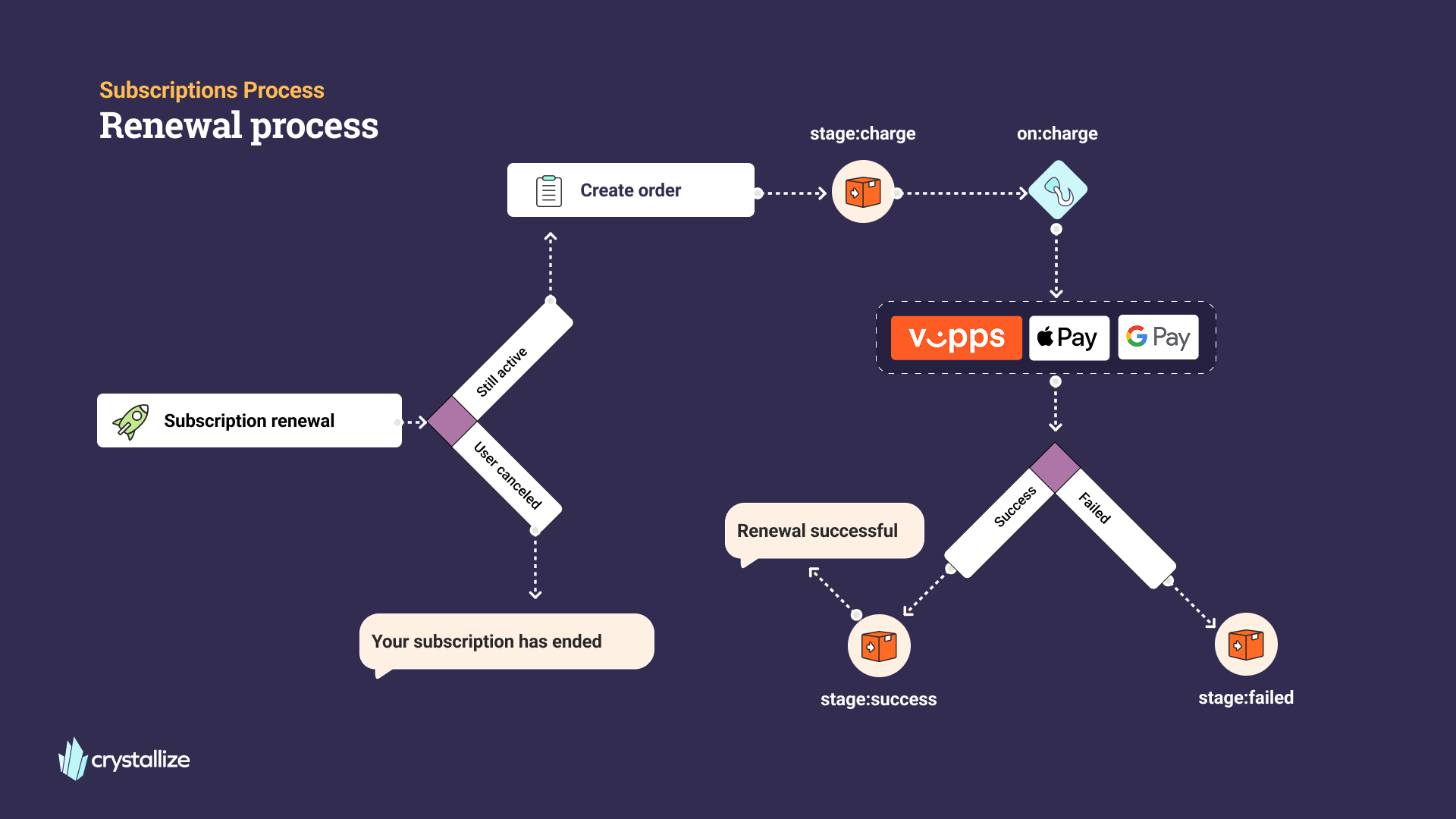
Renewal Flows
At the end of the billing cycle, Crystallize automatically handles subscription renewal.
- A renewal is triggered by the subscription contract.
- If the subscription is still active, a new order is created.
- The payment provider charges the stored token.
- If the charge is successful, the subscription continues and the customer receives confirmation.
- If the charge fails, the contract moves to a failed state and you can define retry logic or customer notifications.
- If the user cancels, the subscription ends after the current period.