Conditional classification Bridge
When relationships come with rules.
The Conditional Classification Bridge is a design pattern for modeling relationships that carry rules and dependencies. It builds on the semantic bridge concept but adds logic that governs how related items interact. This allows you to express product configurations, compatibility rules, ingredient dependencies, or bundles where some parts are optional and others are required.
With this pattern you can model scenarios like a topping that requires another topping, a component that excludes another, or an accessory that can only be selected when the base product supports it. The result is smarter, rule-aware product data that improves both authoring and frontend configuration.
Context and Motivation
Many products contain relationships that are not purely informational. They include logic. A choice may require another choice. Some options are incompatible. Some components are optional but others are mandatory.
Traditional relations cannot express this on their own. Conditional relationships are needed for:
- Product configurators
- Kits with required subcomponents
- Recipe rules
- Compatibility logic
- Optional and mandatory bundle composition
A Conditional Classification Bridge addresses this by storing both the relation and the rule.
The Pattern Explained
At its core the pattern follows the structure:
Item → Bridge → Related items with rules
The bridge is a chunk-based component that stores:
- A relation to another item or variant
- A rule describing how that relation behaves
- Optional metadata for validation or UI hints
Common rule types:
- Requires: Selecting A demands that B is also selected
- Excludes: Selecting A prevents selecting B
- Optional: No constraints
Semantic vs Conditional Bridges
A semantic bridge provides rich relationships and additional metadata.
A conditional bridge goes further by adding rule-aware logic.
Where the semantic bridge enriches meaning, the conditional bridge controls behaviour.
Why this helps
- Authors get a clear way to express structured product logic
- Frontend apps can automatically enforce rules
- Product configurations become predictable and consistent
- You can prevent invalid combinations before they occur
Use Cases
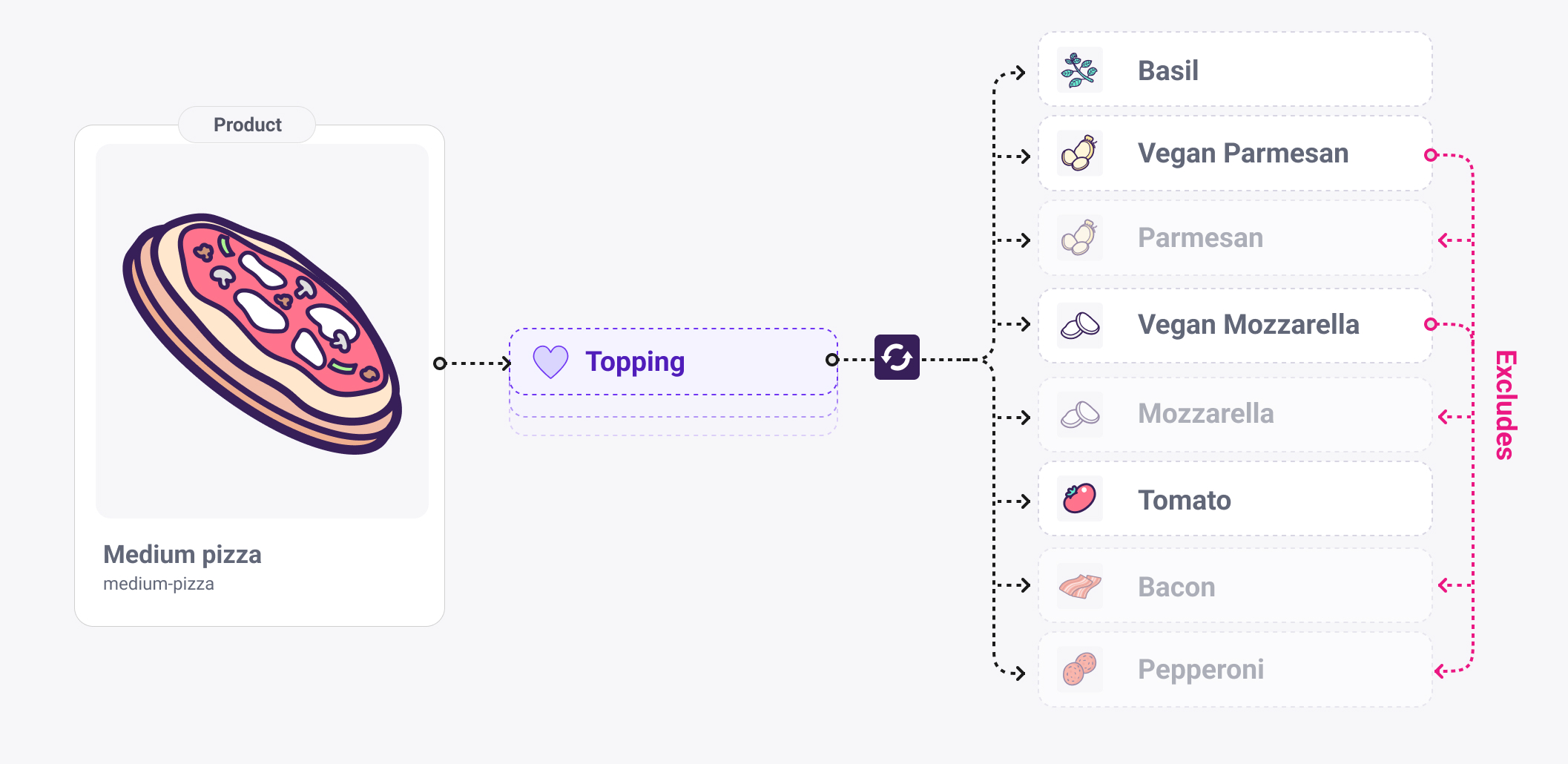
Pizza builder with topping dependencies
A realistic starting point for demoing conditional logic. Examples:
- Chili Requires Cheese
Chili → Requires → Cheese - Vegan Cheese Excludes Meat
Vegan Cheese → Excludes → Meat group - Extra Cheese Requires Regular Cheese
Extra Cheese → Requires → Regular Cheese - Half Pepperoni Requires Split Base
Half Pepperoni → Requires → Split Base - Gluten Free Base Excludes Stuffed Crust
Gluten Free Base → Excludes → Stuffed Crust
Furniture kits
Choose legs and the system automatically adds the correct screws.
Legs → Requires → Screw Set
Product compatibility
Cameras, lenses, chargers, and other accessories where compatibility is key.
Lens X → Requires → Camera body with mount type M
Camera Y → Excludes → Batteries of type Z
Watch the livestream
Keep exploring
Semantic classification bridge
The Semantic Classification Bridge is a data modeling design pattern used to represent complex product attributes in a reusable and scalable way. Instead of relying on flat enums or repeated fields inside product shapes, this pattern separates classification data into dedicated documents that can be enriched, related and shared across many products. This provides better consistency, supports localization, and improves the storytelling capability of product data.
Quantised classification bridge
The Quantised Classification Bridge is a design pattern for modelling composite products in Crystallize. It lets you link one product to another while also expressing how much of each item is included. This enables structured storytelling, nutrition or material breakdowns, bill of materials, kits and bundles, and manufacturing style assemblies. The pattern builds on standard relations, but adds measurable quantity to each link, making the relationship both semantic and precise.