Polymorphic Choice Design Pattern
Polymorphic content modeling helps you create flexible data structures without losing semantic clarity. This page documents the Polymorphic Choice design pattern and explains how to apply it in practice when modeling content and product data in Crystallize.
Polymorphic comes from Greek where poly means many and morph means forms. In Crystallize, polymorphism allows a component to take different shapes while still representing the same semantic concept.
What Polymorphic Choice is
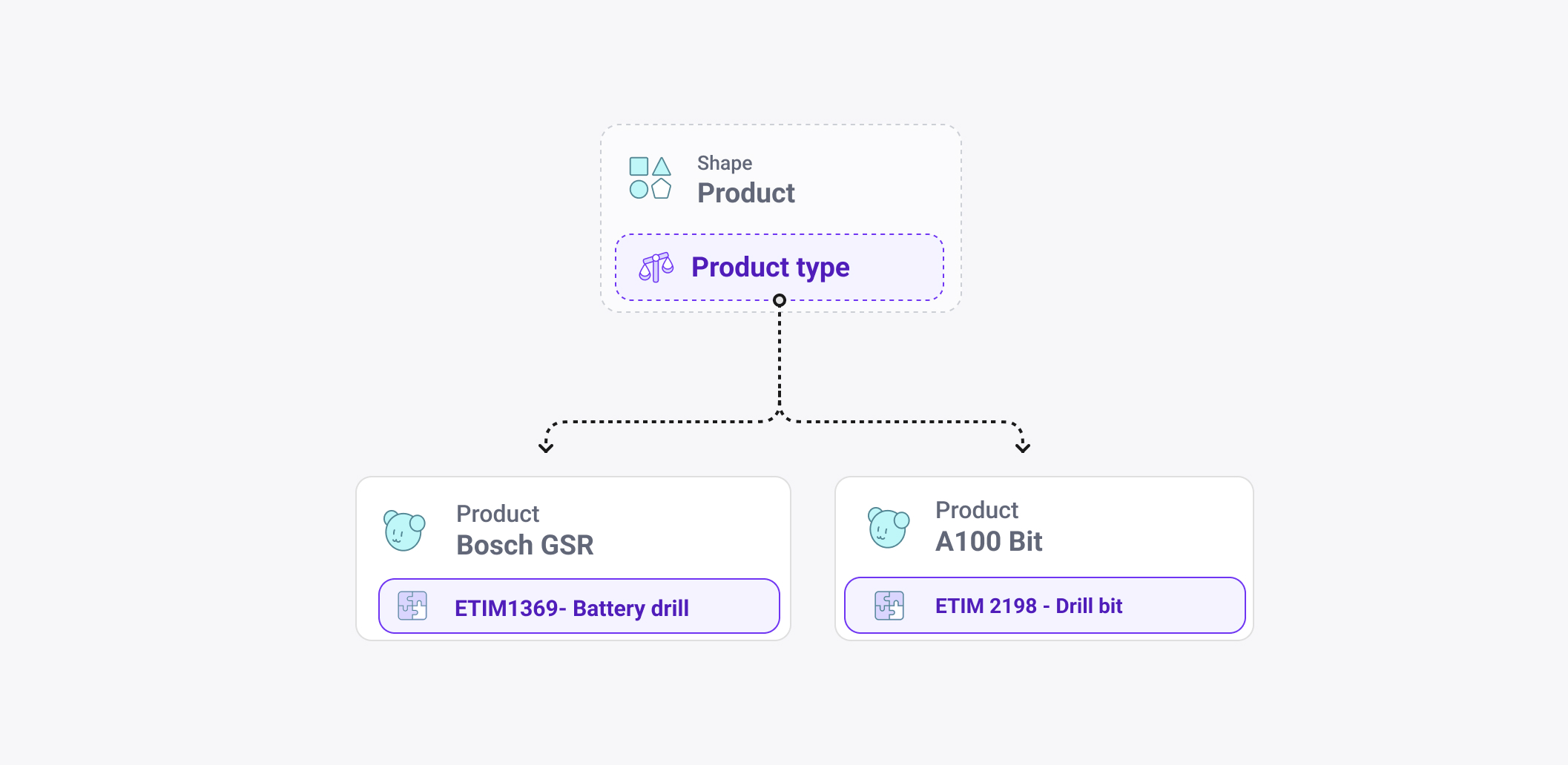
Polymorphic Choice is a content modeling design pattern that lets a single semantic concept take one of several predefined structural forms. The meaning of the component stays the same, but its internal shape changes based on a deliberate selection. In Crystallize this is implemented using the choice component, which enforces that exactly one structure is selected. This gives you flexibility without sacrificing data clarity, predictability, or API stability.
How it works in practice
A choice component defines multiple valid structures for the same concept and ensures that only one can be used at a time. Editors explicitly select the structure they need and are only presented with fields relevant to that choice.
This pattern is especially useful when:
- A concept has multiple valid representations, but they are mutually exclusive
- You want to preserve strong semantics while allowing variation
- Frontend logic and integrations depend on predictable data shapes
A common example is a hero component that can be an image hero, a video hero, or another layout variant. Another example is product modeling based on standards like ETIM, where each product belongs to exactly one class, and each class defines its own fixed property set.
When and why to use it
Use Polymorphic Choice when only one structural form should exist at a time and when semantic integrity matters more than raw flexibility. It works well for product types, standardized data models, and mutually exclusive layouts. Because the selection is explicit, the editor experience is clear and guided, and the resulting data supports clean rendering, comparison, filtering, and integrations.
If multiple structures should coexist or repeat, other polymorphic patterns such as multi choice or stack based modeling are more appropriate.
Livestream recording on the Polymorphic Choice design pattern
Keep exploring
Semantic classification bridge
The Semantic Classification Bridge is a data modeling design pattern used to represent complex product attributes in a reusable and scalable way. Instead of relying on flat enums or repeated fields inside product shapes, this pattern separates classification data into dedicated documents that can be enriched, related and shared across many products. This provides better consistency, supports localization, and improves the storytelling capability of product data.
Conditional classification Bridge
When relationships come with rules.
The Conditional Classification Bridge is a design pattern for modeling relationships that carry rules and dependencies. It builds on the semantic bridge concept but adds logic that governs how related items interact. This allows you to express product configurations, compatibility rules, ingredient dependencies, or bundles where some parts are optional and others are required.
With this pattern you can model scenarios like a topping that requires another topping, a component that excludes another, or an accessory that can only be selected when the base product supports it. The result is smarter, rule-aware product data that improves both authoring and frontend configuration.
Composite classification bridge
Adding semantic meaning to item relations
The Composite classification bridge allows you to create item relations that carry meaning. Instead of linking items without context, you can describe what the relation represents. This pattern is useful when you want rich storytelling, structured data and predictable frontend behavior.
Examples include linking a book to its contributors and describing their role, or linking a product to materials and describing where each material is applied such as lining, sleeve or collar.
This guide walks through the pattern, the schema setup and how to query and use this structure for more expressive product models.
Quantised classification bridge
The Quantised Classification Bridge is a design pattern for modelling composite products in Crystallize. It lets you link one product to another while also expressing how much of each item is included. This enables structured storytelling, nutrition or material breakdowns, bill of materials, kits and bundles, and manufacturing style assemblies. The pattern builds on standard relations, but adds measurable quantity to each link, making the relationship both semantic and precise.